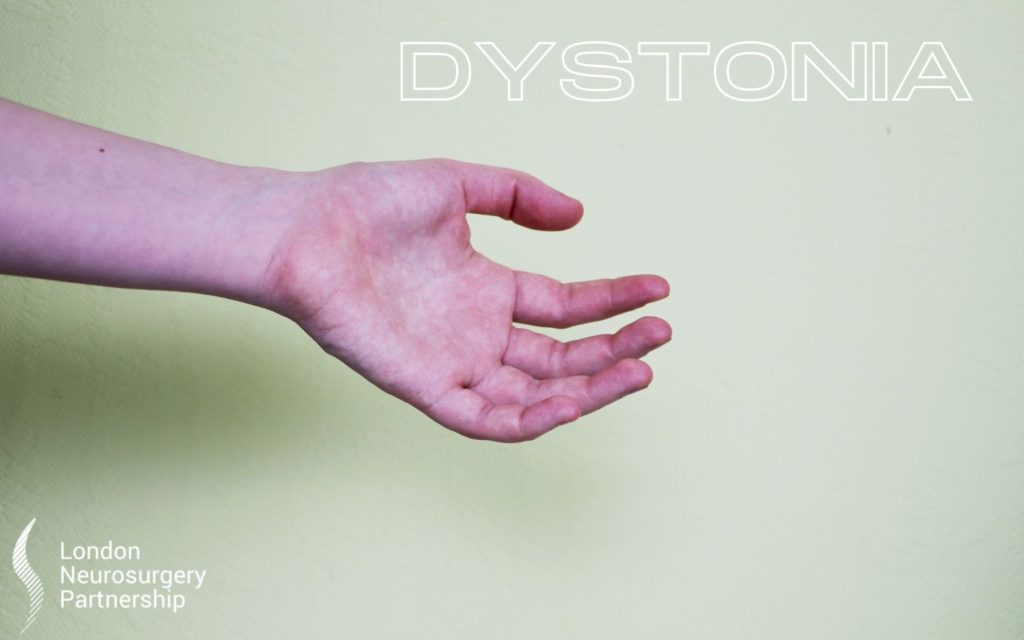

Dystonia is a neurological movement disorder which causes uncontrolled and sometimes painful muscle movements. Dystonia can affect the whole body, one part of the body, or a number of adjacent areas. It is estimated to affect at least 70,000 people in the UK. Richard Selway and Professor Ashkan are world renowned experts in this field.
What causes dystonia?
Dystonia occurs due to faulty signals from the brain which cause our muscles to spasm and pull on the body incorrectly. However, we do not fully understand why this happens. In a small number of cases, dystonia does have a clear cause as it can be related to another medical condition (stroke or tumour), a side-effect of certain medications and genetics (dystonia can be inherited).
Symptoms
Dystonia is usually a lifelong condition that can occur at any age. Symptoms may be constant or occasional and can be triggered by certain activities or stress. Common symptoms include;
- Uncontrolled, painful muscle cramps and spasms
- Blinking that cannot be controlled
- Abnormal fixed positions eg. your neck twisting to one side or your feet turning inwards
- Uncontrolled shaking (tremors)
Diagnosis
Your consultant will ask you about your medical history and symptoms, they will also want to know if anyone in your family has dystonia as it can be hereditary. Dystonia can be diagnosed through blood and urine tests, your consultant may also want to do a MRI scan and CT scan to rule out other conditions causing your symptoms. A further test called an electromyography exam may be required, which measures the electrical activity within your muscles.
Treatment
Treatments for dystonia will not cure the condition but they will help to relieve symptoms. The main treatments are;
- Botulinum toxin injections. These act as muscle relaxants which stops contractions.
- Medicine. This can also help to relax muscles in a larger part of the body.
- Therapy. Physiotherapy, occupational therapy and speech and language therapy may also help.
- Surgery. Deep brain stimulation surgery where electrodes are implanted in the brain and a small generator sends electrical impulses to control spasms.
This article is intended to inform and give insight but not treat, diagnose or replace the advice of a doctor. Always seek medical advice with any questions regarding a medical condition.
Back to brain conditions or functional neurosurgery conditions.




0 Comments